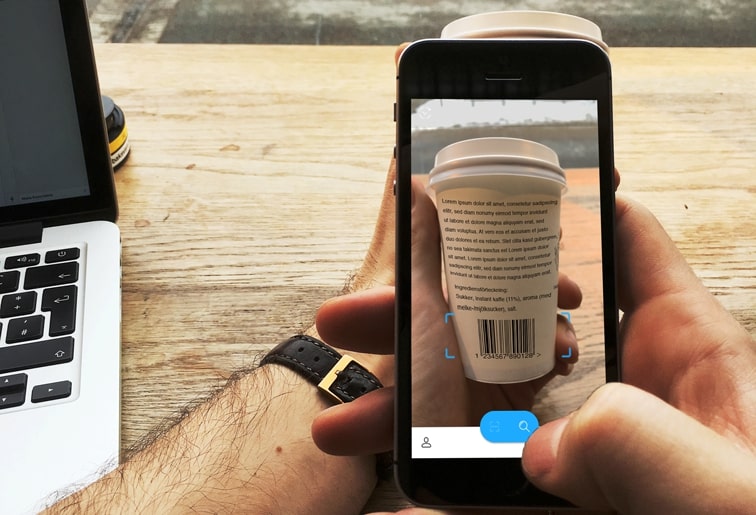
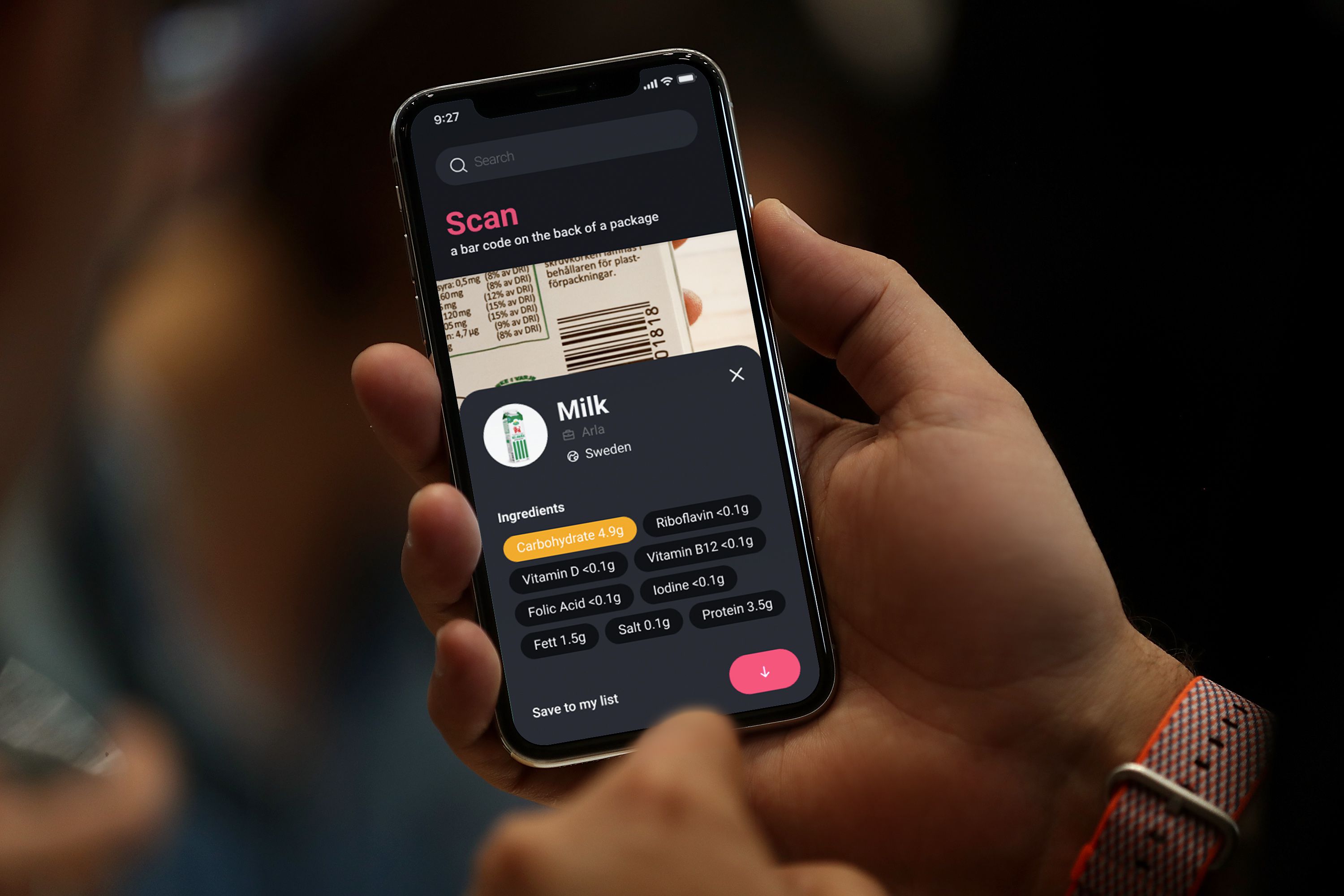
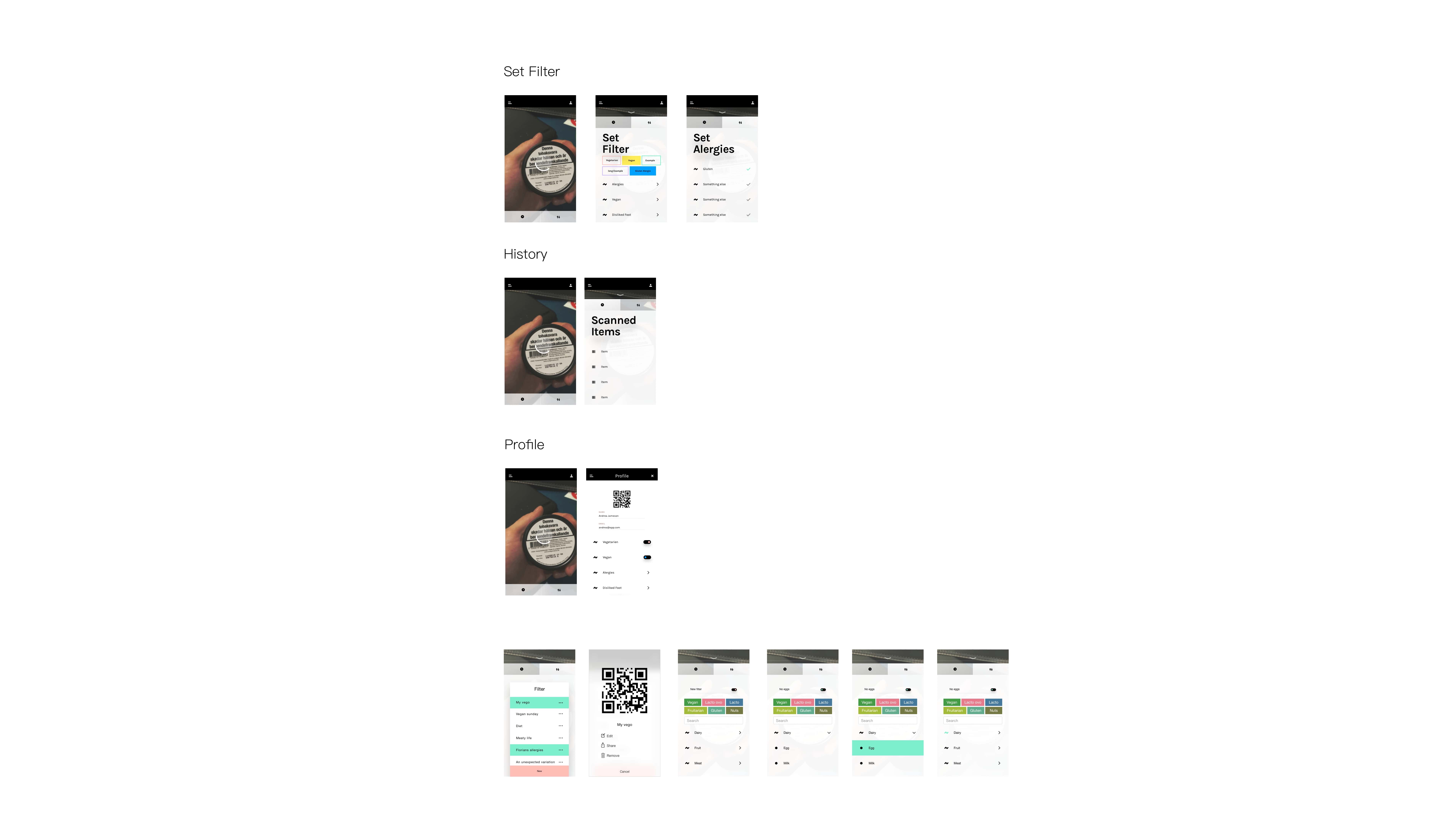
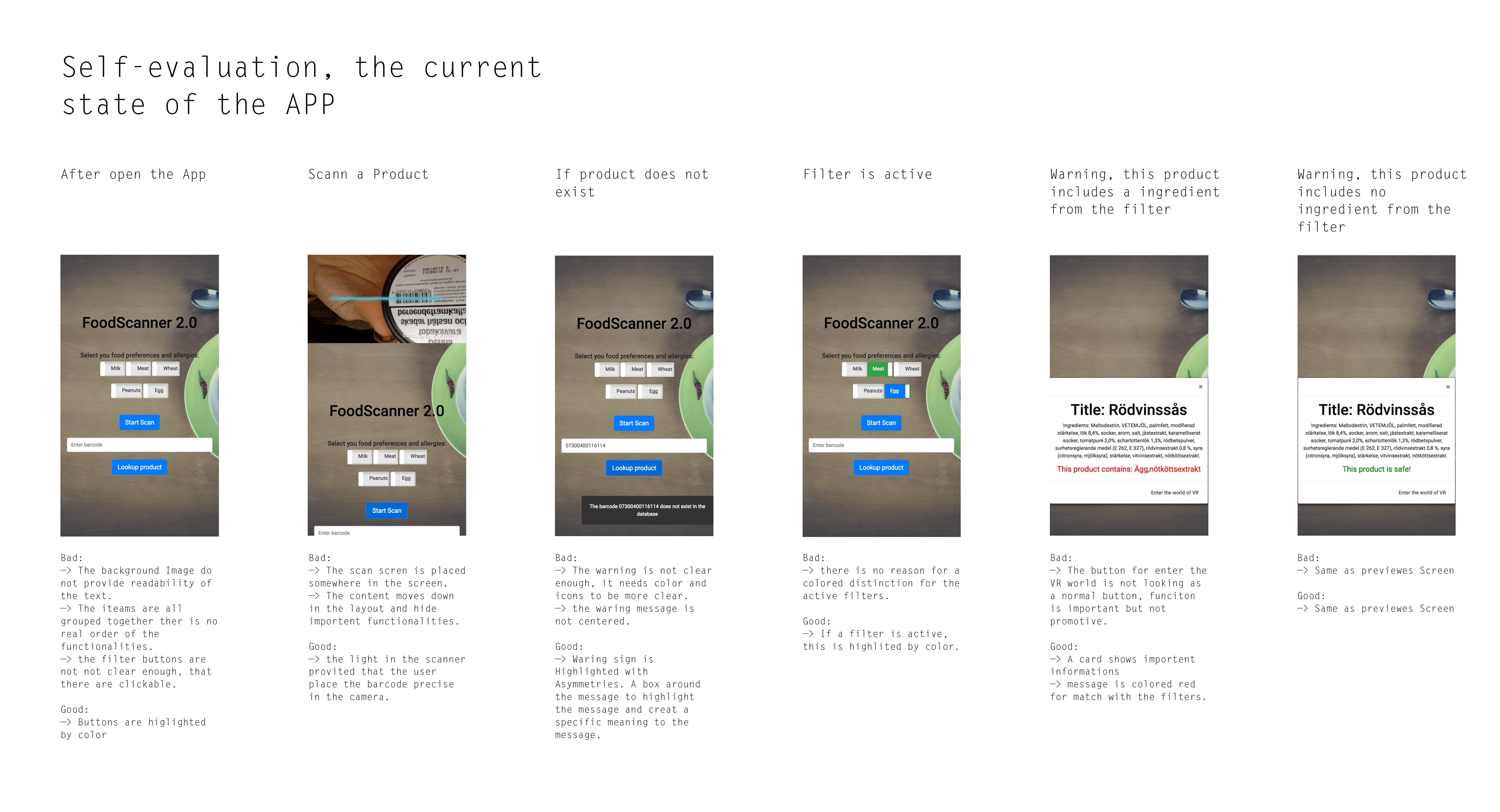
Beyond this functionality, the app can also store filters from other users. This makes it possible for someone can go shopping for another person.
If there is a match with the filters and the user really wants or needs the product. The app gives recommendations for similar products which the user is allowed to eat.
In cooperation with:
Carl Albertsson, Carl Lindvall, Florian Wachter, Pontus Åberg, Simon Larsson Takman